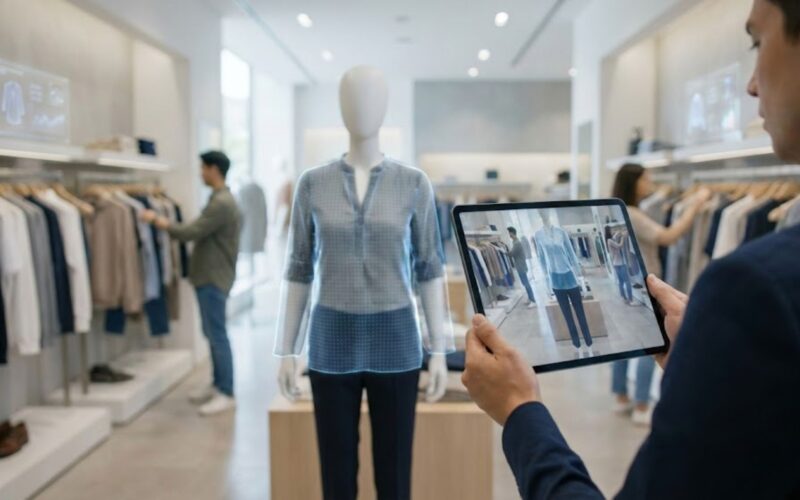
Augmented Reality (AR) is changing how retailers interact with customers by bridging physical products and digital experiences. Retailers are increasingly deploying AR features such as virtual try‑on, interactive product exploration, and contextual overlays to help shoppers make confident decisions.
Recent forecasts indicate that global AR in the retail market revenue could exceed $105 billion by 2033, growing at over 32% annually, driven by immersive shopping innovations and widespread mobile adoption.
This blog provides a full view of how AR is currently applied in retail, the technology components that support it, and how a structured development approach enables successful AR solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Augmented Reality (AR) enhances retail by providing immersive experiences like virtual try-ons and real-time product visualisation.
- AR reduces return rates and boosts conversion by helping customers make more informed purchase decisions.
- Integration with existing retail systems (e.g., inventory, e-commerce platforms) ensures seamless customer interactions across channels.
- Effective AR solutions require addressing challenges like device compatibility, user adoption, and system integration.
What Are the Primary Use Cases for AR in Retail?
AR delivers measurable improvements by bringing product information and interaction directly into the shopper’s field of view.
Retailers use AR to cut uncertainty, display products across contexts, and deepen shopper engagement.
1. Virtual Try‑Ons and Fitting Rooms
Customers can use their smartphone or tablet camera to preview how a product looks on their body or in their environment. This is especially common for:
- Apparel and accessories
- Eyewear
- Makeup and beauty products
Virtual try‑on reduces guesswork for fit, style, and appearance, addressing a major barrier in online shopping.
2. Product Visualization in Real Spaces
AR lets shoppers place 3D product renderings in their real space via camera overlays. Common applications include:
- Furniture in a living room
- Appliances on a kitchen counter
- Decor on walls or shelves
By contextualizing size and look before purchase, consumers make more informed decisions.
3. Interactive Product Information
Instead of static images and text, AR can show:
- 3D exploded views
- Customization options
- Usage demonstrations
This type of engagement helps customers grasp features that are difficult to convey through traditional media.
4. In‑Store AR Assistance
In physical stores, AR can assist customers by:
- Guiding them to product locations
- Displaying dynamic offers
- Enabling instant scanning for inventory details
This aligns digital convenience with physical store experiences.
5. Marketing and Engagement Campaigns
Brands use AR in campaigns to increase dwell time and interest. Retailers report that 3D/AR content can raise conversion rates by around 94% for featured products compared to standard listings.
Have a great product idea, but unsure if it’ll work? Codewave’s Design Thinking Led Product Development helps transform your idea into a user-approved product. With 400+ global business partnerships, we focus on delivering high adoption and engagement through user validation and prioritized features.
Let’s get started with Codewave today.
Also Read: Steps to Become a Mobile App Developer and Create an App
How AR Improves Customer Experience in Retail
Augmented Reality enhances the customer experience by removing key barriers that typically hinder confidence, clarity, and satisfaction throughout the shopping journey.
Rather than just visual enhancements, AR adds context and interactive layers of information that help customers make decisions faster and with greater confidence.
1. Increase in Confidence and Purchase Decisions
Consumers often abandon purchases because they are unsure how a product will look, feel, or fit in real life. AR addresses this by enabling scenario‑based product previews:
- Visual context: Customers can place digital versions of furniture, electronics, or décor in their own space using their camera, helping them see how a product fits their size, colour, and design requirements.
- Virtual fitting: Apparel, eyewear, and makeup brands allow customers to “try on” items with real‑time AR overlays, making decisions more tangible than flat images alone.
2. Reduction in Return Rates
One of the biggest operational pain points for online and omni‑channel retailers is the volume of returns. Traditional online shopping lacks the sensory assurance that physical inspection provides. AR helps reduce that gap:
- Retailers implementing AR for preview and fitting report25% lower return ratescompared with those that do not use AR tools.
- When customers better understand how a product fits their needs before checkout, they are more likely to keep the item, saving logistics and restocking costs.
This outcome has a measurable impact on profitability, not just customer satisfaction.
3. Blending Online and Physical Shopping Journeys
AR bridges the divide between e‑commerce and brick‑and‑mortar experiences, creating interaction models that support choice anywhere:
- Online-to-offline continuity: Customers can visualise a product online and then use AR wayfinding tools or in-store overlays to locate it in a physical store.
- In‑store interactive layers: Retailers can present digital labels, animated demonstrations, or customisation options to customers scanning shelf items. This enriches browsing beyond what printed tags or QR codes alone can provide.
4. Personalised Engagement at Scale
Beyond generic interactions, AR also enables tailored experiences that respond to individual shopper context:
- Custom content, such as colour or size options, personalised recommendations, and situational overlays (e.g., care instructions or compatibility information), can be surfaced based on user actions.
- Dynamic AR experiences can adapt as customers navigate through a store or product catalogue, making recommendations relevant in real time rather than generic.
Also Read: AI in UX Design: Exploring Benefits and Challenges
With a clear understanding of how AR benefits customers, let’s examine the technology stack behind these powerful solutions.
What Is the Typical AR Technology Stack Used in Retail?
A comprehensive AR solution combines development platforms, device capabilities, supporting frameworks, and backend services.
Core AR Development Platforms
| Platform | Primary Use | Strengths |
| ARCore | Android AR apps | Strong environmental understanding and motion tracking support |
| ARKit | iOS AR development | Optimised for Apple devices with advanced light estimation |
| Vuforia | Cross‑platform AR | Reliable 3D and image target tracking across devices |
These tools provide the foundation for AR features such as spatial recognition, camera overlays, and motion tracking.
3D Rendering Engines
Most retailers use game‑grade 3D engines like:
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
These engines handle complex rendering and object interaction logic, making AR visuals responsive and realistic.
Machine Vision and Analytics
Computer vision components detect surfaces and objects. Machine learning can further enable:
- Body segmentation for fitting rooms
- Object recognition for product overlays
- Behaviour analysis for personalisation
Cloud and Backend Services
AR solutions often rely on cloud services for:
- Content delivery
- User session tracking
- Real‑time synchronisation across devices
Cloud APIs also support analytics that help retailers refine engagement flows.
Hardware Components
Retail AR applications target devices such as:
- Smartphones and tablets with AR support
- Dedicated AR glasses (emerging use cases)
Device performance affects the user experience, particularly in rendering quality and detection accuracy.
Also Read: AI/VR Development: How AI is Transforming Virtual Gaming
Having covered the technical side, let’s look at how retailers can develop and implement AR solutions effectively.
How Should Retailers Approach AR Solution Development?
Developing AR for retail goes beyond technical implementation. A structured process ensures outcomes align with business aims.
Step 1: Define Business Goals and Use Cases
Start by identifying specific outcomes, such as:
- Increasing online conversion rates
- Reducing return rates
- Enhancing in‑store assistance
Defining clear metrics at the outset informs the AR features you prioritise.
Step 2: UX and Experience Design
AR experiences require thoughtful user flows. Key design principles include:
- Easy onboarding for AR features
- Clear instructions for camera usage
- Minimal friction in controls and gestures
Poor UX can negate the benefits of advanced AR capability.
Step 3: Choose the Right Development Frameworks
Tool selection should align with:
- Target device ecosystem (iOS, Android, cross‑platform)
- Required features (surface detection, body tracking, object recognition)
- Performance benchmarks
For example, Unity, when paired with ARCore and ARKit, supports a broad range of devices.
Step 4: Build Prototypes and Test Iteratively
Prototyping allows teams to validate assumptions with real users. Iterations should focus on:
- Tracking stability
- Rendering fidelity
- Interaction comfort
Testing early avoids downstream complexity.
Step 5: Deployment and Monitoring
Once validated, roll out AR features with built‑in monitoring. Analytical data helps refine:
- Engagement funnels
- Feature usage patterns
- Drop‑off points
Monitoring tools provide visibility into how customers interact with AR features.
Facing challenges with mobile app development?Codewave delivers consumer-grade apps 3X faster and at 30% less cost with 100% quality assurance. We ensure seamless performance, scalability, and security while focusing on user satisfaction.
What Challenges and Practical Considerations Should Retailers Address?
Introducing Augmented Reality in retail promises value but also brings real technical, organizational, and financial complexities.
Effective AR deployment requires balancing innovation with the realities of hardware diversity, legacy systems, user acceptance, cost evaluation, and integration workstreams.
1. Technical Limitations
AR systems rely on hardware and sensors that differ widely between devices. Retailers must account for variation in smartphone capabilities and environmental conditions.
Key technical barriers include:
- Device fragmentation: The quality of AR experiences varies significantly across Android and iOS devices due to differences in camera capability, sensor accuracy, and processing power.
- Performance challenges: Rendering AR content in real time is resource‑intensive and can cause lag, overheating, or rapid battery depletion on mid‑range devices.
- Tracking and environmental consistency: Reliable surface detection and object tracking can be less effective in low-light or environments without distinct visual cues.
These limitations mean developers must prioritize performance optimization, progressive feature degradation (simpler fallback visuals), and extensive QA across common device profiles to ensure consistent user experiences.
2. Integration with Existing Retail Systems
AR must operate in tandem with a retailer’s existing backend infrastructure to deliver accurate, real‑time information.
Systems that typically need to integrate with AR platforms include:
- Inventory management and stock systems to show real‑time availability.
- E‑commerce and POS platforms to align product visuals with actual listings.
- Customer personalisation engines to provide tailored content during AR sessions.
Integration challenges come from legacy systemsthat lack modern APIs or consistent product data hierarchies. Retailers often need middleware or data synchronisation layers to ensure AR overlays reflect the latest pricing, variants, and availability data.
3. User Adoption and Accessibility
Not all customers will immediately engage with AR features, especially if they are unfamiliar with them or perceive them as complex.
Retailers should address adoption barriers by:
- Providing clear in‑app prompts and simple instructions for first‑time AR use.
- Offering non‑AR alternatives (e.g., 3D models or enhanced product galleries) for users with unsupported devices.
- Prioritizing accessibility with options like voice commands, captions, and alternative control schemes to ensure inclusion.
User education and subtle onboarding flows help increase feature discovery and uptake without overwhelming customers.
4. Cost and ROI Evaluation
Retail AR initiatives involve substantial investment in development, 3D content creation, testing, and support infrastructure. Many retailers underestimate these costs or fail to connect spend to business outcomes.
Costs and financial considerations include:
- Development complexity, especially when AR features involve markerless tracking, collision detection, or complex spatial overlays.
- High‑quality 3D assets and content updates for large product catalogues.
- Maintenance overhead for platform updates and device compatibility.
Retailers should measure AR ROI against specific performance metrics such as:
- Conversion rate changes post‑AR deployment.
- Impact on return rates (AR experiences tend to lower uncertainty, reducing returns).
- Engagement metrics such as session duration and repeat usage.
How Codewave Supports Retailers with AR and Extended Reality Development
Codewave offers Extended Reality (XR) development services, including Augmented Reality (AR), to help retailers enhance customer engagement. We create interactive AR features, such as visual overlays and real-time product visualisations, that seamlessly integrate with shopping platforms.
Our solutions improve the customer journey, enabling better product interactions and more informed purchase decisions. With Codewave, retailers can use AR to boost engagement and drive sales.
What Codewave Delivers for Retail AR
- Extended Reality Expertise: Codewave provides XR solutions spanning AR, VR, and MR development across platforms, including Unity, ARCore, ARKit, and WebXR, enabling immersive experiences on mobile and web.
- Custom Application Development: Integration of AR features into existing retail apps or custom AR apps designed to meet specific business requirements, backed by the company’s foundation in UX/UI design and cloud‑ready architectures.
- Design‑First Approach: By combining design thinking with XR technologies, Codewave focuses on intuitive user flows and contextual experiences that reduce friction for shoppers and strengthen digital interaction points.
- System Alignment: AR experiences are engineered to align with backend systems, ensuring product visuals and information reflect real‑time catalog, inventory, and personalisation data. (reflects general developer approach based on Codewave’s digital transformation offerings)
Explore our portfolioto discover how we’ve helped clients implement AR and other digital transformation solutions.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is transforming the retail experience by allowing customers to engage with products in more meaningful ways. From virtual try-ons to interactive displays, AR helps shoppers make better decisions and improves satisfaction.
As consumers increasingly expect immersive shopping experiences, retailers that adopt AR can stand out in a competitive market. By integrating AR seamlessly with existing systems, retailers can enhance both online and in-store experiences.
Codewave can help you design and implement AR solutions tailored to your business needs, driving customer engagement and improving sales.Get in touch with usto explore how AR can elevate your retail strategy.
FAQs
Q1: How can AR enhance in-store experiences compared to online shopping?
A1: AR brings digital elements into physical spaces, enabling customers to interact with products in real time, guiding them to items in the store, and providing instant product details, enhancing the in-store shopping experience.
Q2: Can AR technology be used for personalized marketing in retail?
A2: Yes, AR can create personalized experiences by overlaying tailored recommendations, offers, and product suggestions based on a customer’s preferences or previous interactions, thereby enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
Q3: What devices are required to use AR in retail?
A3: AR in retail can be accessed through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. While smartphones and tablets are most common, more advanced experiences may require dedicated AR hardware or headsets.
Q4: How does AR improve customer loyalty in the retail sector?
A4: By offering immersive, personalized shopping experiences that resonate with customers, AR helps build stronger emotional connections with the brand, which can lead to higher customer loyalty and repeat visits.
Q5: Is AR integration costly for small retail businesses?
A5: While AR implementation does require investment, it’s becoming more accessible to small businesses with advances in mobile AR apps and cloud-based solutions that reduce development costs and make it easier to scale.
Codewave is a UX first design thinking & digital transformation services company, designing & engineering innovative mobile apps, cloud, & edge solutions.